
ANIMAL PROTEIN VS PLANT PROTEIN
It’s a debate we see all around us these days: animal vs plant protein, what’s better? In a world of rising vegetarianism, veganism and meat consumption, the conclusion doesn’t seem clear cut. One thing is certain though, one of the main sources of animal protein is animal meat, and animal meat consumption at the current rate is detrimental to our environment. So what’s the solution?
In regards to health, both animals and plants can be high-quality protein sources, but not all proteins are created equal. Some are considered to be healthier than others, and some are complete proteins whereas others are incomplete.
Let’s start from the beginning.
What is Protein?
Protein is one of the five food groups that makes up a balanced diet – in addition to carbohydrates, fruits and vegetables, dairy and healthy fats. Proteins are essential for our bodies to function and stay healthy. They have many uses within our bodies that help it run smoothly and efficiently. Although protein exists in all parts of our bodies, from our muscles to our hair, our bodies do not store protein. This means we have to consume it in our diets.

Protein can be acquired from animal and plant sources. All proteins are made up of amino acids that are broken down when eaten. There are twenty two types of amino acids which are broken down into essential and non-essential, and our bodies need all of them. However, our bodies cannot produce the nine essential amino acids. Instead, these come from the protein we consume.
Protein sources can be complete or incomplete depending on which amino acids they contain. A complete source of protein contains all nine types of amino acids. It’s important to fill our bodies with the right ratios of amino acids from proteins so that it can build and repair itself.
Where does Protein Come from?
Protein sources are plentiful from both plants and animals, although the number and type of amino acids within them differ. Common sources of protein are:
- Red meat, e.g. beef
- Poultry, e.g. chicken
- Eggs
- Fish
- Lentils
- Beans
- Soy
- Nuts
- Legumes
- Certain vegetables, e.g. peas & spinach
- Grains, e.g. quinoa
- Tofu
Many people underestimate how many sources of protein come from plants. It is definitely possible to enrich your diet with all the protein it needs purely from plants alone. We all know that protein comes from animal meat, fish, and eggs too, but it’s important to know that that’s not where protein sources end.
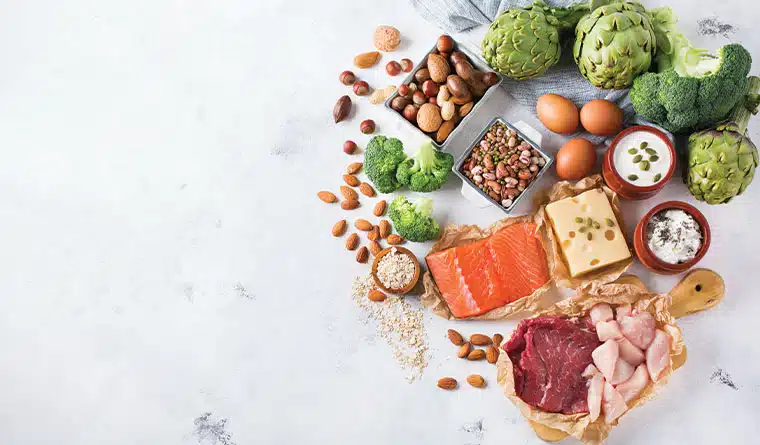

Animal Protein vs Plant Protein
Animal proteins are complete proteins, whereas plant proteins are incomplete. This does not mean plant proteins are not as good for your health. It simply means you need a wider variety to give your body the right ratio of amino acids.
Animal proteins are complete proteins because they contain all nine of the essential amino acids our bodies require. Since they provide our bodies with what they need, they are not entirely bad for you. At the same time, they can also carry health risks. The question on the tip of many tongues is: is animal protein bad for you?
Generally, animal protein that comes from poultry, egg and fish is considered to be healthier than red meat. Diets high in red meat are often linked to an increased risk of heart disease, diabetes and stroke.
Flipping the question around, many people want to know: is plant protein good for you? Can you consume enough protein from plants alone? Put simply, the answer is yes. Plant proteins are good for you and you can have a protein-rich diet fulfilled by plants. However, you need more variety of them in your diet in order to give your body the full amount of amino acids it needs.
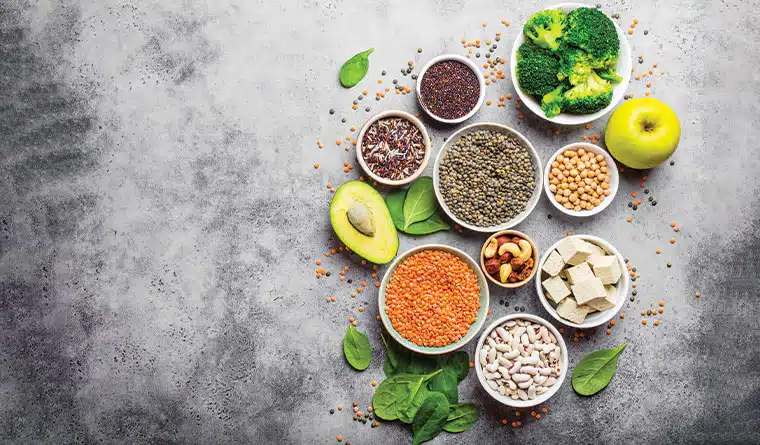

As we’ve established, plant proteins and animal proteins have different pros and cons. Beyond amino acids, plant and animal proteins also differ in the minerals and nutrients they offer too. Plant proteins are often full of nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants, all of which are good for your health. They can help reduce the risk of the very same diseases that red meat is believed to increase the risk of. Animal proteins enrich your diet with vitamin B12, vitamin D and Zinc, which are all beneficial for your health too.
Environmental Impacts of Plant vs Animal Protein
It’s a well known fact that the meat industry at the current rate of mass production is one of the biggest contributors to the climate crisis. For more information on why eating meat is bad for the environment, we’ve got you covered on our blog.
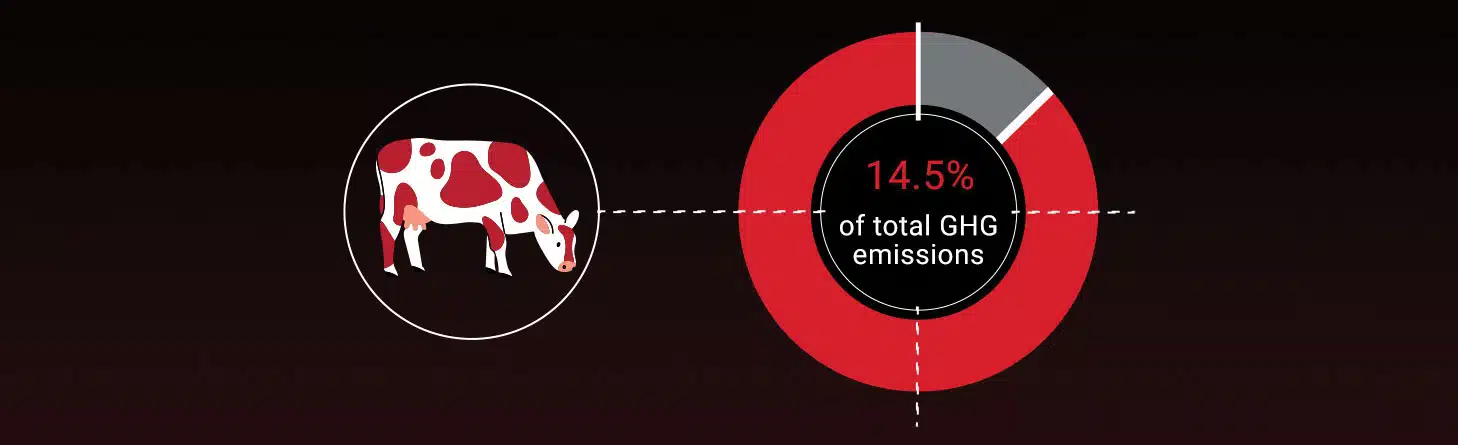
Approximately 14.5% of Global Greenhouse Gas emissions come from the meat and dairy industry. It takes four times more water to produce beef than, for example, lentils or other plant-based proteins. For context, 72 million tons of beef is produced each year. It also takes a staggering 75 times more energy to produce meat than corn. What’s more, beef requires 15,000 liters of water per kilo of end product, whereas vegetables only require 300 liters per kilo.
If we don’t reduce our global meat consumption, it’s likely that we will find ourselves in a food shortage crisis in under thirty years. That’s why plant protein is growing in importance around the world, and more and more options like New-Meat™ are cropping up on the market to make an animal meat-free life a lot easier and tastier.
Final Thoughts
Both animal protein and plant protein can be good for you, and both come with their own pros and cons. There’s no denying that the environmental impact of consuming plant protein is less than that of consuming animal protein. Which, given the climate emergency we find ourselves in, is reason enough to increase our consumption of plant protein over animal protein.
Luckily, there are tons of plant protein alternatives to real meat out there to make the transition from a meat eating diet to a plant-based diet a lot easier. REDEFINE MEAT™ offers nearly every cut of meat a cow can offer – including minute steak – and is indistinguishable from animal meat in taste and texture. It’s called New-Meat™ and you can find it in restaurants near you.
FAQs
What is protein?
Protein is one of the five food groups that makes up a balanced diet. It’s essential for our bodies to function and stay healthy. It has many uses within our bodies that help it run smoothly and efficiently. Although protein exists in all parts of our bodies, from our muscles to our hair, our bodies do not store protein. This means we have to consume it in our diets.
Where does protein come from?
Protein can come from both plants and animals, although the number and type of amino acids within them differ. Common sources of protein are red meat, poultry, fish, lentils, soy, nuts, legumes, grains and tofu.
Is plant protein as good as animal protein?
Yes. As long as there is a variety of plant protein being consumed, then the human body will receive the nine essential amino acids, just as it would from consuming animal protein. Plus, by consuming plant-based proteins, one can reduce or avoid the added hormones, antibiotics or saturated fats often associated with beef, and increase the consumption of fiber and essential vitamins.
What is the key difference between plant protein and animal protein?
Animal proteins are complete proteins whereas plant proteins are incomplete. That means animal proteins have the nine essential amino acids our bodies need, whereas plant proteins don’t contain them all within one source. You therefore have to eat a wider variety of plant protein to provide your body with the required amino acids. Also, animal proteins are linked to more health risks such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and stroke. Plant proteins are generally considered to be more sustainable, too, because the meat production industry is one of the biggest contributors to the climate crisis.




